Titanium Grade 2 – Titanium Alloys| Austral Wright Metals
 |
Product Data Sheet – Titanium Alloys |
Titanium Grade 2 UNS-R50400 |
Titanium Alloy Grade 2 is commercially pure titanium. It has outstanding corrosion resistance and useful strength (similar to austenitic stainless steels) at low density. It has good weldability and is easily formable. It is the most commonly used grade of titanium.
If you need Titanium Alloy Grade 2 for your next project, get in touch with us today via our Enquiry Form or call on 02 9827 0790.
Typical Applications of Titanium Grade 2Most of the applications of this grade are in the chemical industries. The most common uses are reactor autoclaves, piping and fittings, valves, heat exchangers and condensers.
Chemical CompositionASTM B338 – Seamless & welded titanium & titanium alloy tubes for condensers & heat exchangers
Specified Minimum Mechanical Properties(ASTM B338 – Seamless & welded titanium & titanium alloy tubes for condensers & heat exchangers)
DescriptionTitanium grade 2 is a commercially pure titanium grade. It has excellent corrosion resistance in oxidising conditions, and is effectively immune from stress corrosion cracking, pitting corrosion and crevice corrosion in chloride solutions below 70°C. Titanium grade 2 is widely used in heat exchangers, where despite the low thermal conductivity of titanium the efficiency of heat transfer is high due to good strength, high resistance to erosion corrosion and the fouling resistance of the hard, smooth surface.
At room temperature grade 2 is an alpha alloy. It transforms to beta phase at 913 ±15°C, and the alpha phase returns on cooling 890 ±15°C.
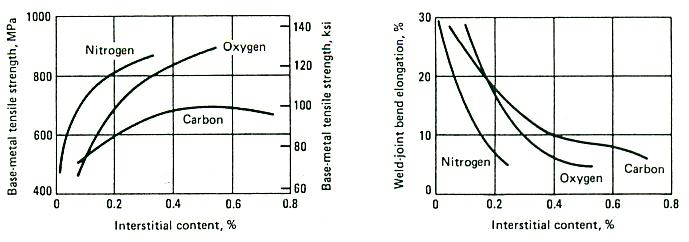
Titanium is reactive, with a very high affinity for oxygen, which forms a skin of very stable and highly adherent oxide. The skin gives excellent corrosion resistance, despite the reactivity of the metal. The oxide layer forms spontaneously and rapidly on exposure to the atmosphere. However, when new parent metal is exposed to anhydrous conditions or in the absence of air, rapid corrosion may occur. Care should also be taken if titanium is to operate in contact with hydrogen, as hydrogen embrittlement from hydride formation can increase strength, with loss of ductility.
AvailabilityAustral Wright Metals can supply this commercially pure titanium alloy as plate, sheet and strip, rod and bar, seamless and welded pipe, weld fittings, seamless and welded tube, forging billet and forgings. It is widely used as tube in condensers and heat exchangers.
Pressure VesselsAS1210 & ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code pre-qualify titanium 2 for use in pressure vessels up to 300°C. AS4041 Pressure Piping qualifies the alloy to 325°C. Corrosion ResistanceTitanium grade 2 has excellent resistance to general corrosion, with low or negligible loss rates in many media. See Austral Wright Metals data sheet “Corrosion of Titanium and alloys” for more detail. The table at the end of this data sheet illustrates the excellent erosion-corrosion performance of grade 2 in seawater.
Physical Properties
Erosion Corrosion Rates of Unalloyed Titanium, Grade 2
FabricationTitanium grade 2 is forged by conventional processes within the narrow temperature range 815 – 900°C. Titanium and its alloys generally are more difficult to forge than both aluminium and alloy steels, due to the narrow temperature range, and high strain rate and temperature dependence of strength. Hot forging leaves a thick, extremely hard layer of titanium oxide on the surface, called “alpha case”. It is usually removed by pickling in a mixture of nitric and hydrofluoric acids. As supplied, titanium alloys are usually annealed, and can be readily cold formed in conventional machines using standard methods. When cold formed the alpha case does not form and pickling is not needed, except to remove embedded carbon steel pickup, which can cause pitting corrosion.
MachinabilityTitanium grade 2 is readily machinable by conventional methods. It is similar to austenitic stainless steels for machinability. Like stainless steel, titanium has a low thermal conductivity and heat dissipation is poor, so generous use of coolant is recommended. Sharp tools are essential. Cuts should be deep and continuous, with low cutting speeds.
WeldabilityTitanium grade 2 is readily weldable by GMAW and GTAW processes. Preheat or post weld heat treatment are not needed. The area immediately surrounding the welds must be CLEAN, free from all grease and shop dirt, including pencil marks. Abrasive cleaning can be used, or solvent cleaning or pickling with a mixture of nitric and hydrofluoric acids. A trailing gas shield must be applied to all areas above 450°C in addition to the normal welding torch gas shield, to prevent heavy oxidation during cooling. Matching filler metal to AWS ERTi-2 is used. The gas shield must be low in hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen, all of which readily dissolve in titanium and cause embrittlement.
Heat TreatmentTitanium grade 7 is annealed at 650 – 760°C, still air-cooled. Pickling to remove the alpha case may be needed before further fabrication or machining. Stress relief at 480 – 595°C, air-cooled, may be required to improve dimensional stability for critical components.
Effects of Interstitial Elementson the strength and ductility of unalloyed aluminium
ASTM Product Specifications
|