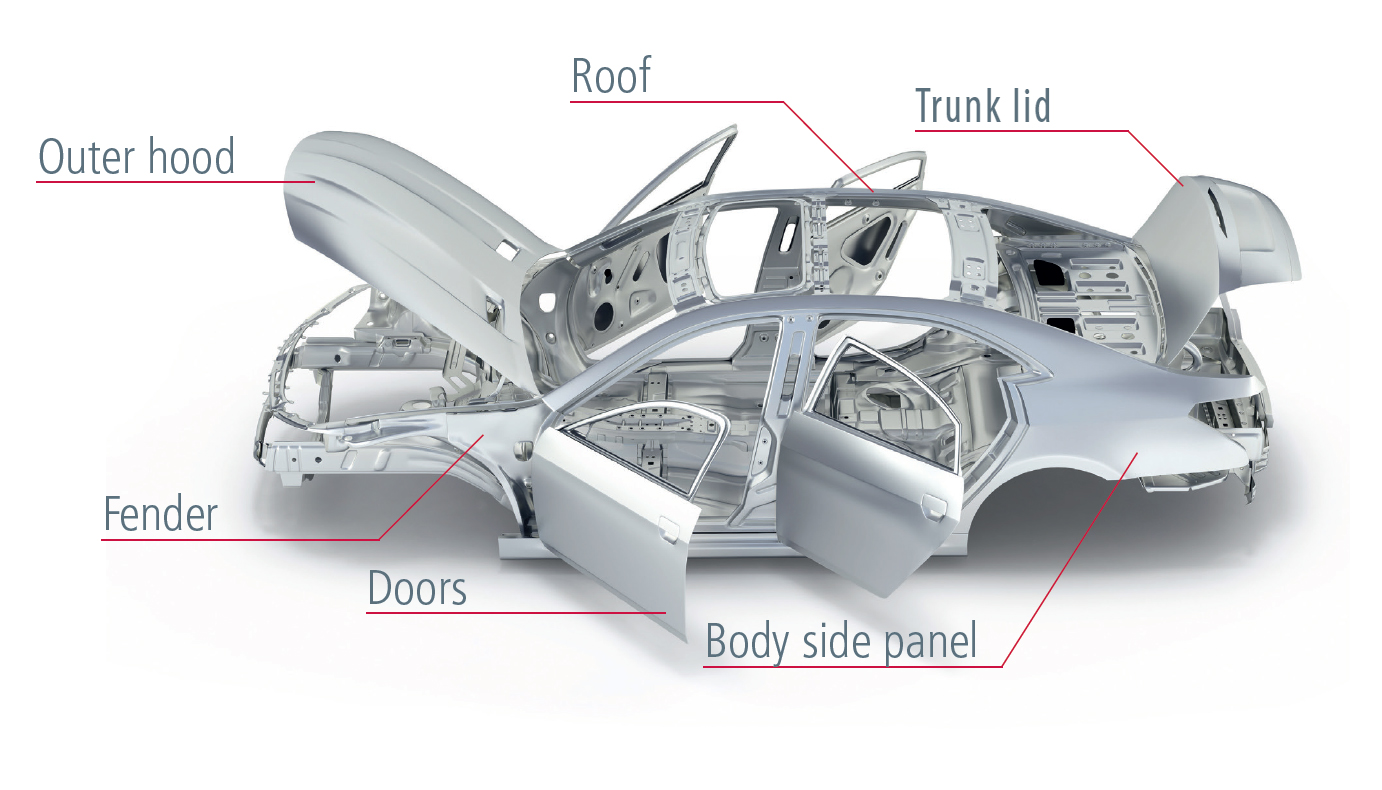
What is aluminium used for?Aluminium is a versatile, widely used and abundant metal with a range of applications across various industries. We will not discuss the use of aluminium oxide, which is a compound of aluminium and oxygen found in minerals such as bauxite found in the earth’s crust and used in producing aluminium. Some of the most common uses of aluminium include:
Transportation:Aluminium is used in the production of cars, trucks, trains, boats, and airplanes because of its strength, light weight, and corrosion resistance. Aluminium has a low density, making it significantly lighter than steel. Using aluminium in transportation vehicles helps reduce overall weight, leading to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. It is commonly used in car bodies, aircraft, and bicycles. Aluminium naturally forms a protective oxide layer that helps resist corrosion. This makes it suitable for outdoor applications, especially in marine environments where exposure to moisture and saltwater is common. Aluminium is highly malleable and can be easily formed into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs and streamlined structures in vehicles. This flexibility in shaping is particularly beneficial in the aerospace industry. Although aluminum is not as strong as steel, it offers a favorable strength-to-weight ratio. This means that aluminium structures can provide sufficient strength while keeping weight low. It contributes to improved performance and efficiency in transportation vehicles. Aluminium is highly recyclable, and the recycling process consumes significantly less energy compared to primary production. This makes aluminium a sustainable choice for transportation, aligning with environmental goals. In transportation, aluminium production is used in various components such as body panels, engine blocks, wheels, suspension systems, and aerospace structures. The use of aluminium helps manufacturers meet stringent regulations for fuel economy and emissions, while also enhancing vehicle performance and durability.
Packaging:Aluminium is used extensively in the packaging industry because it is lightweight, easy to shape, and provides an effective barrier against moisture, air, and light. Aluminium is commonly used in packaging for beverages, including cans for carbonated drinks and beer. It is also used for pharmaceutical packaging, cosmetics, food containers, and flexible packaging such as blister packs and aluminium foil wraps. The use of aluminium in packaging helps preserve product integrity, enhance shelf appeal, and contribute to sustainable packaging solutions.
Construction:Aluminium is used in construction because it is lightweight, strong, and durable. It is commonly used in window frames, roofing, siding, and gutters. Aluminium is used in various construction applications, including window frames, curtain walls, roofing, cladding, structural elements, and interior components. It offers a combination of durability, aesthetic appeal, and sustainability, making it a popular choice for modern construction projects. Electrical and Electronics:Aluminium is used in electrical transmission lines, electronic devices, and heat sinks because it is a good conductor of electricity and dissipates heat quickly. Aluminium is used in various electrical applications, including power transmission lines, electrical cables, bus bars, switchgear, transformers, motors, and generators. While copper is still commonly used for many electrical applications, aluminium offers advantages in terms of weight, cost, and corrosion resistance, making it a viable alternative in certain scenarios. Proper design considerations and installation techniques are essential when using aluminium to ensure its effective and safe use in electrical systems.
Consumer Goods:Aluminium is used in a wide range of consumer goods, including kitchen utensils, beverage cans, and foil. Aluminum is used in a wide range of consumer goods, including electronic devices, kitchenware, furniture, sporting goods, packaging, automotive components, and personal accessories. Its combination of lightweight, durability, aesthetic appeal, and recyclability makes aluminum a popular choice for manufacturers aiming to create high-quality and sustainable consumer products.
Overall, aluminium’s unique combination of properties makes it a valuable material for a variety of applications across numerous industries.
What are the properties of aluminium?Aluminium has several unique properties that make it useful for a variety of applications. Here are some of the key properties of aluminium:
Overall, the unique combination of properties of aluminium makes it a valuable material for a wide range of applications across various industries.
Disadvantages of AluminiumWhilst aluminium has many advantages over other material, it is important to understand some of its limitations:
It’s important to note that many of these disadvantages can be mitigated or managed through proper design, surface treatments, alloying, and other techniques. Aluminum continues to be widely used in various industries due to its favorable properties and versatility.
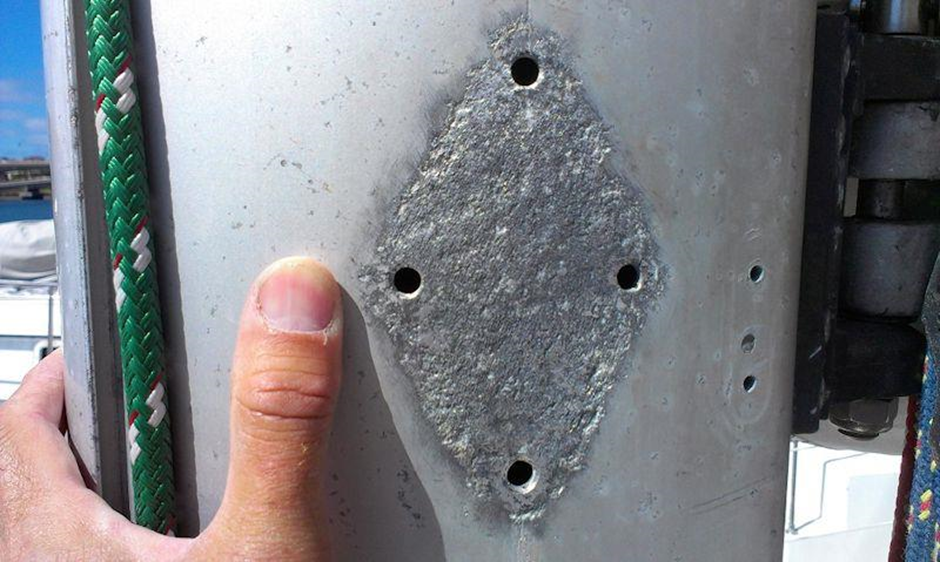
What happens when aluminium is in contact with other metals?When aluminium comes into contact with other metals, a process called galvanic corrosion can occur. Galvanic corrosion happens when two dissimilar metals come into contact in the presence of an electrolyte, such as saltwater or acidic solution. In this process, the aluminium acts as an anode, which means it will corrode faster than the other metal, which acts as a cathode. This is because the electrons will flow from the aluminium to the cathode metal, leading to the breakdown of the aluminium. The severity of galvanic corrosion depends on several factors, including the type of metal, the amount of surface area in contact, and the type of electrolyte present. In some cases, the corrosion can be relatively mild and have little effect on the structural integrity of the aluminium. In other cases, the corrosion can be severe and lead to the failure of the aluminium component. To prevent galvanic corrosion, it is important to use appropriate materials and coatings to separate the dissimilar metals or to avoid exposing the aluminium to electrolytes that can cause corrosion.
What are the most common grades of aluminium?Aluminium is available in various grades, each with different properties and suitable for different applications. Some of the most common grades of aluminium are:
These are just a few examples of the most common grades of aluminium. The choice of the right grade depends on the specific application requirements, such as strength, corrosion resistance, formability, and cost. |